GIGABYTE is committed to mitigating the impacts caused by business operations on climate change. Visionary management policies and effective response plans have been adopted for effectually promoting climate-rated management and adaptation measures.
GIGABYTE released its first GIGABYTE TCFD Report independently in 2023. The Report aims to meet the expectations and information needs of stakeholders, comply with Taiwanese and international sustainability disclosure standards and regulations, and, by strengthening communication, contribute to the continuous optimization of GIGABYTEʼs climate change responses, management capabilities, operational resilience, and market competitiveness.
CDP assessment results in recent years
| Dimension | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Change | A- | A- | A- | B |
| Water Security | / | B | B | B |
| Supplier Engagement | A- | A- | A | A- |
Group Climate Commitment and Management
GIGABYTE has set a greenhouse gas reduction target of a 50% reduction in carbon emission by 2025 with 2009 as the base year. A separate short-term target was set in 2016 under the “333 Reduction Plan” with GIGABYTE promising to reduce carbon emissions, water consumption, and waste production by 3% each compared to the previous year. The concise targets help us track our carbon reduction progress and performance.
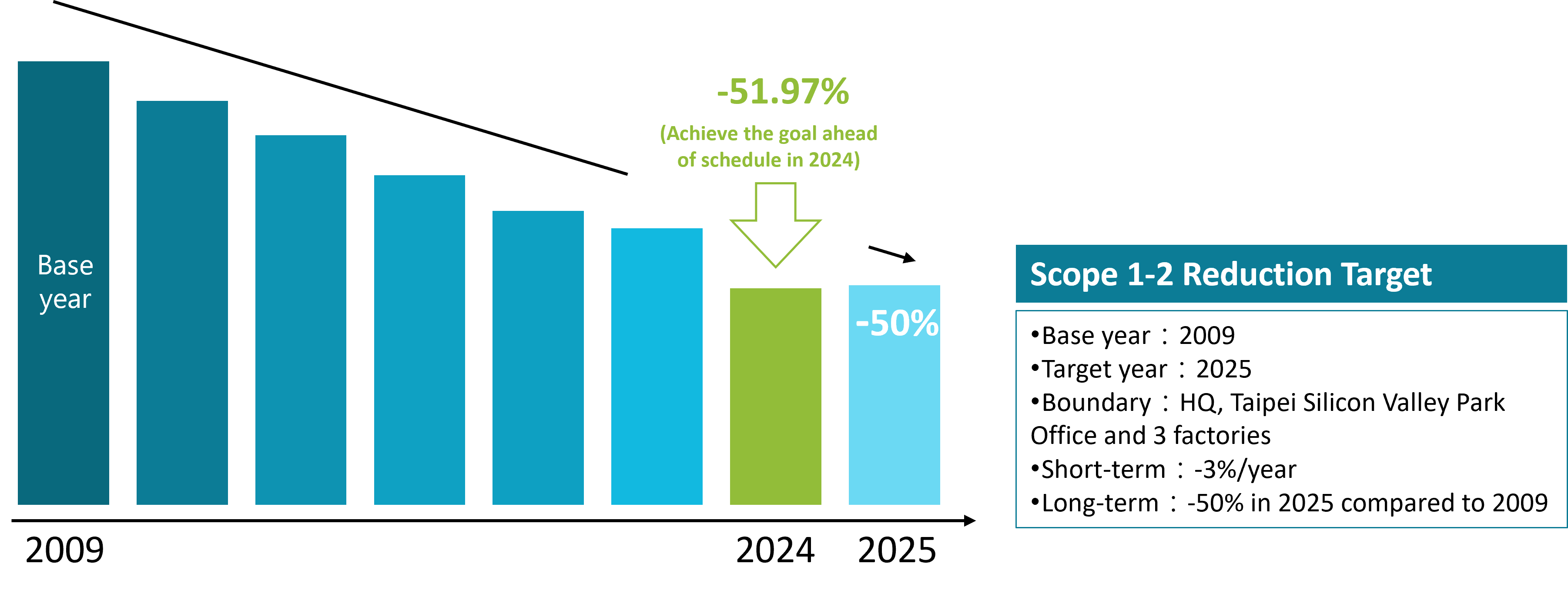
In 2024, GIGABYTE reduced its GHG emmission by 51.97% compared to the base year, achieving its long-term reduction target of 50% one year ahead of schedule. In response to the global call for companies to align with the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), which promotes setting emission reduction goals based on scientific methods to keep global warming well below 1.5°C, GIGABYTE has taken proactive steps. Although the company has not officially announced a Science Based Target, it has adopted tools and target review standards recommended by SBTi to assess the gap between its current reduction goals and the science-based decarbonization pathway, serving as a basis for future adjustments.
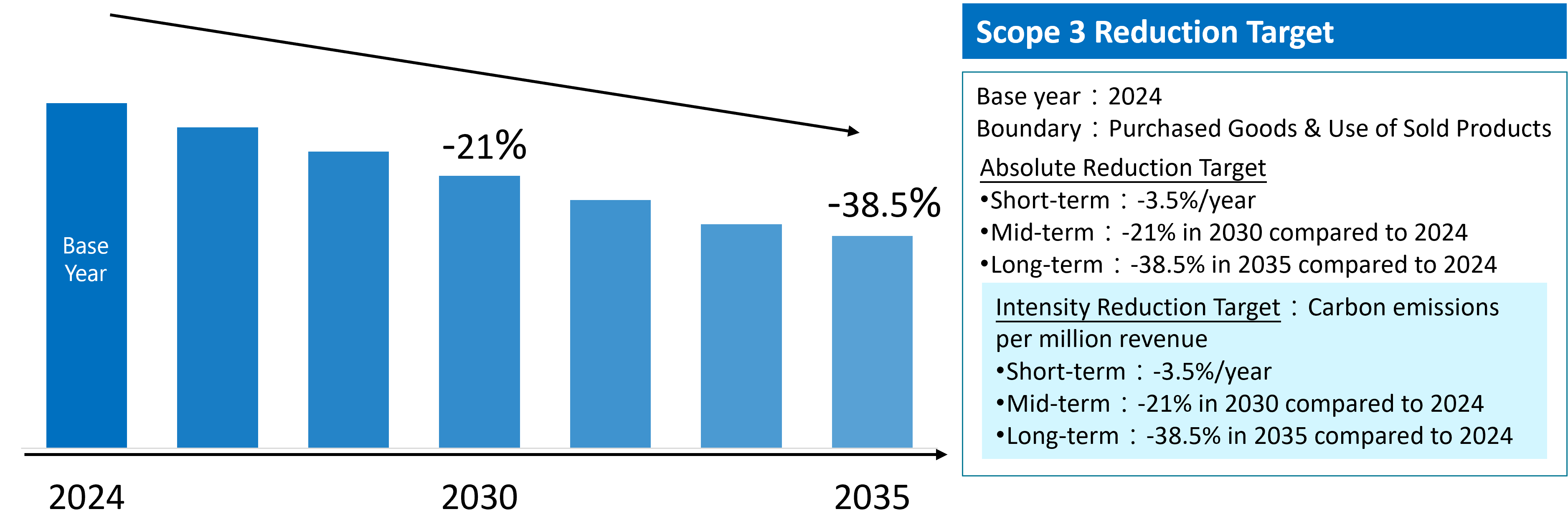
Given the early achievement of its mid- to long-term goals, GIGABYTE has updated its base year to 2020 and set new targets: a 42% reduction in Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions by 2030, and a 63% reduction by 2035. For Scope 3 emissions, 2024 has been designated as the base year, with both absolute and intensity reduction targets established. (Due to GIGABYTE’s recent business growth and changes in organizational boundaries for carbon inventory, it is estimated that emissions will change by more than 5% in 2026. At that time, the base year and reduction targets will be updated accordingly.)
Scope 1-2 GHG Reduction Target | Base year 2020
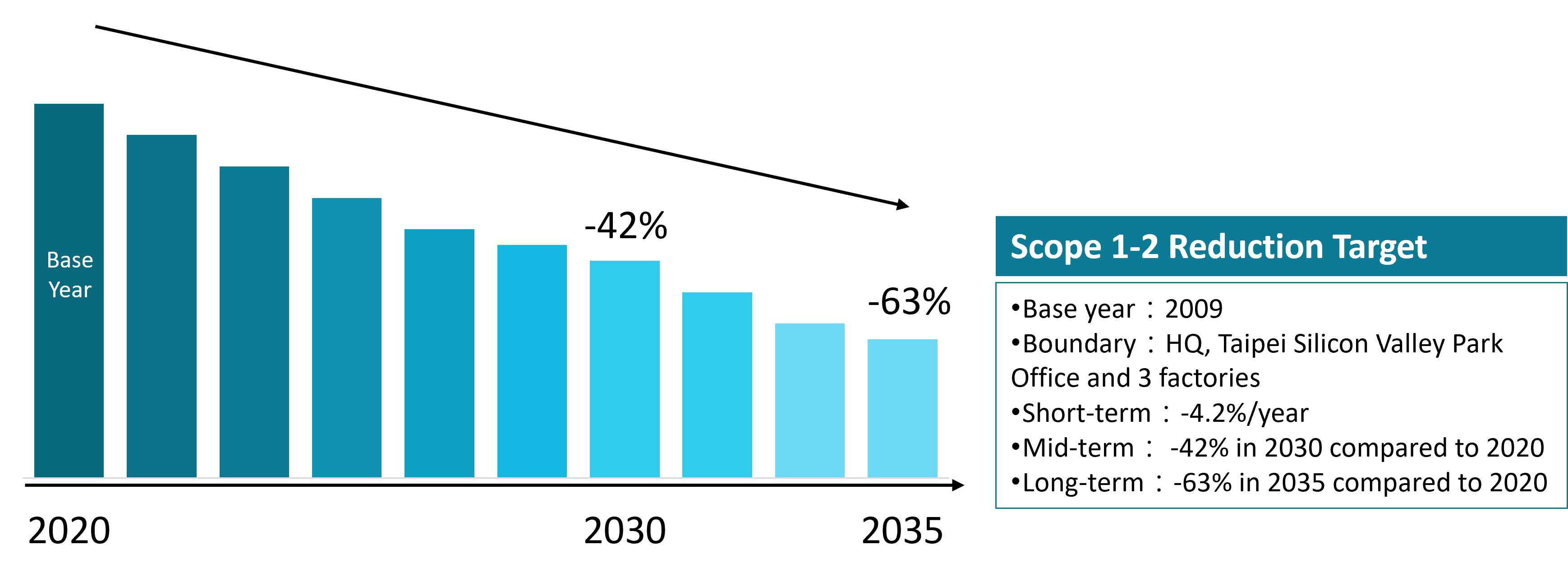
Scope 3 GHG Reduction Target | Base year 2024
Climate Management Strategy
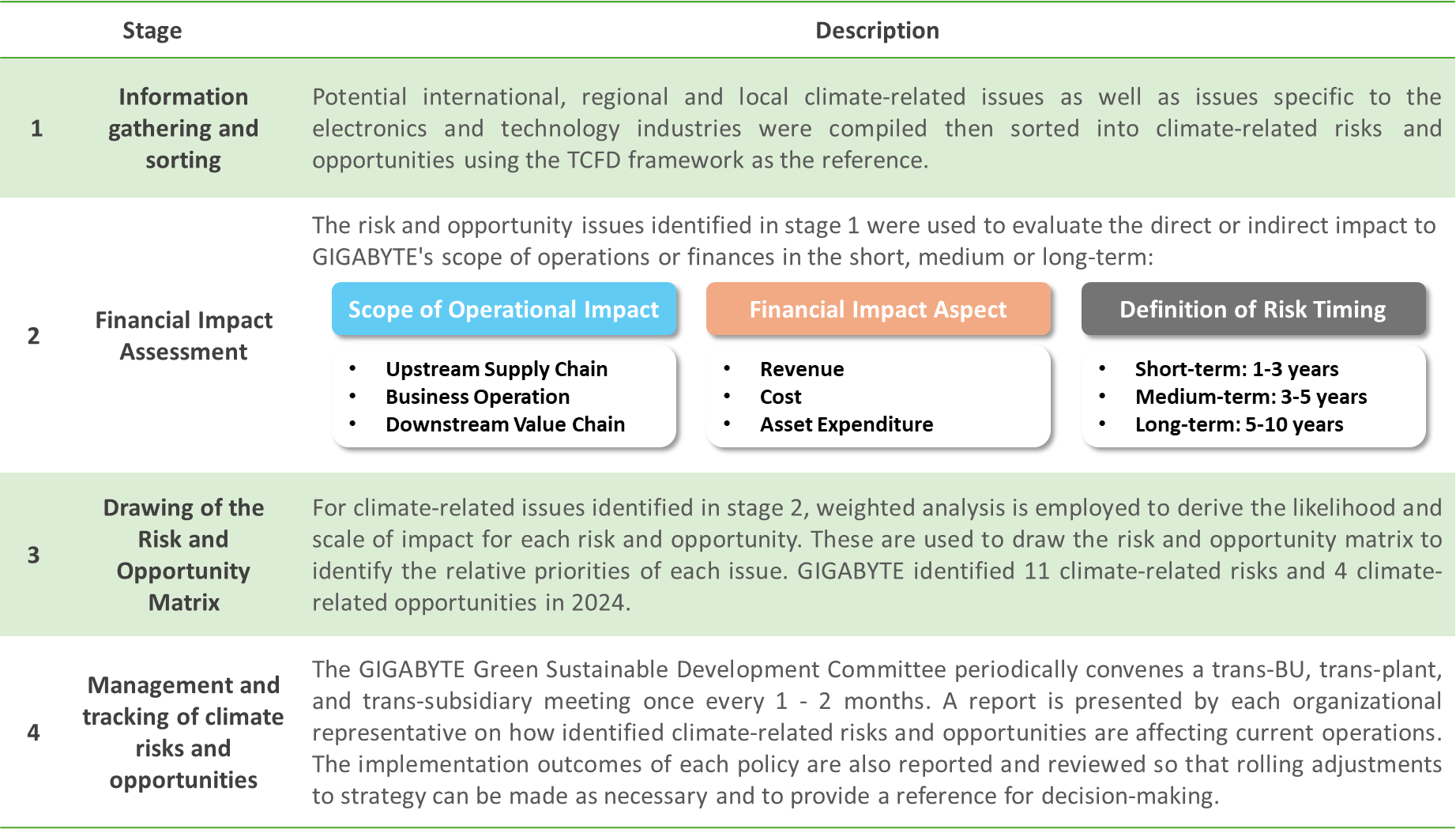
GIGABYTE has designated climate risk as a material operating risk. Climate change and global warming problems are affecting directly on the value chain as a whole from upstream suppliers to company operations and downstream demand. In addition, such sheer scope and scale of impact, there is also added urgency from the fact that human lifestyle, social culture, and economic activities around the world are already being impacted in tangible ways as well. To obtain a full picture of how climate risks may affect the Companyʼs operations or the opportunities that those may create, GIGABYTE identifies climate-related risks and opportunities that will significantly affect finances, change business strategies or models, or pose impacts on the value chain. The planning of corresponding response strategies and management measures are then prioritized. Annual reviews and re-assessments are also conducted through climate scenario analysis.
Process of Climate-related Risk Identification
2024 Climate Risk Matrix
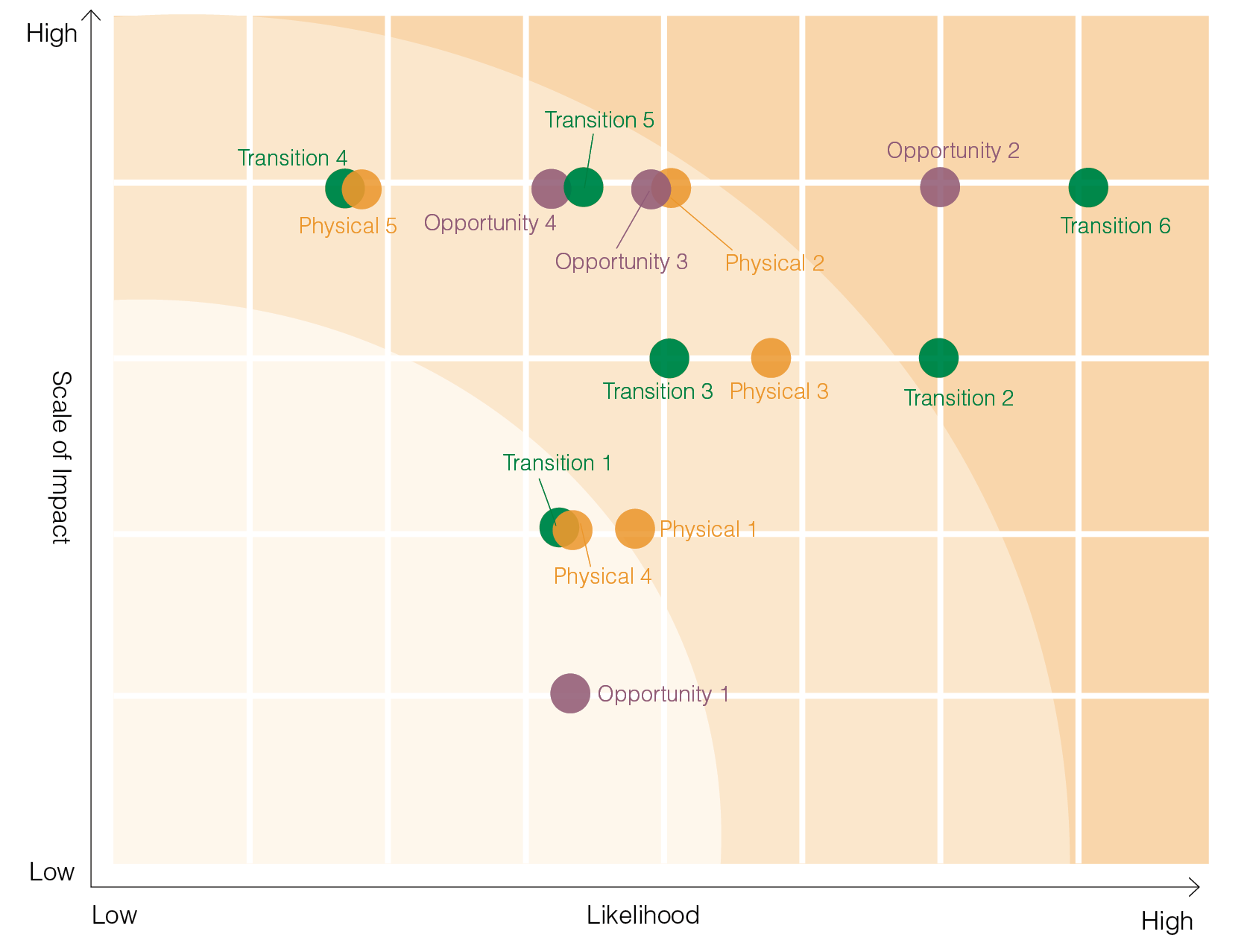
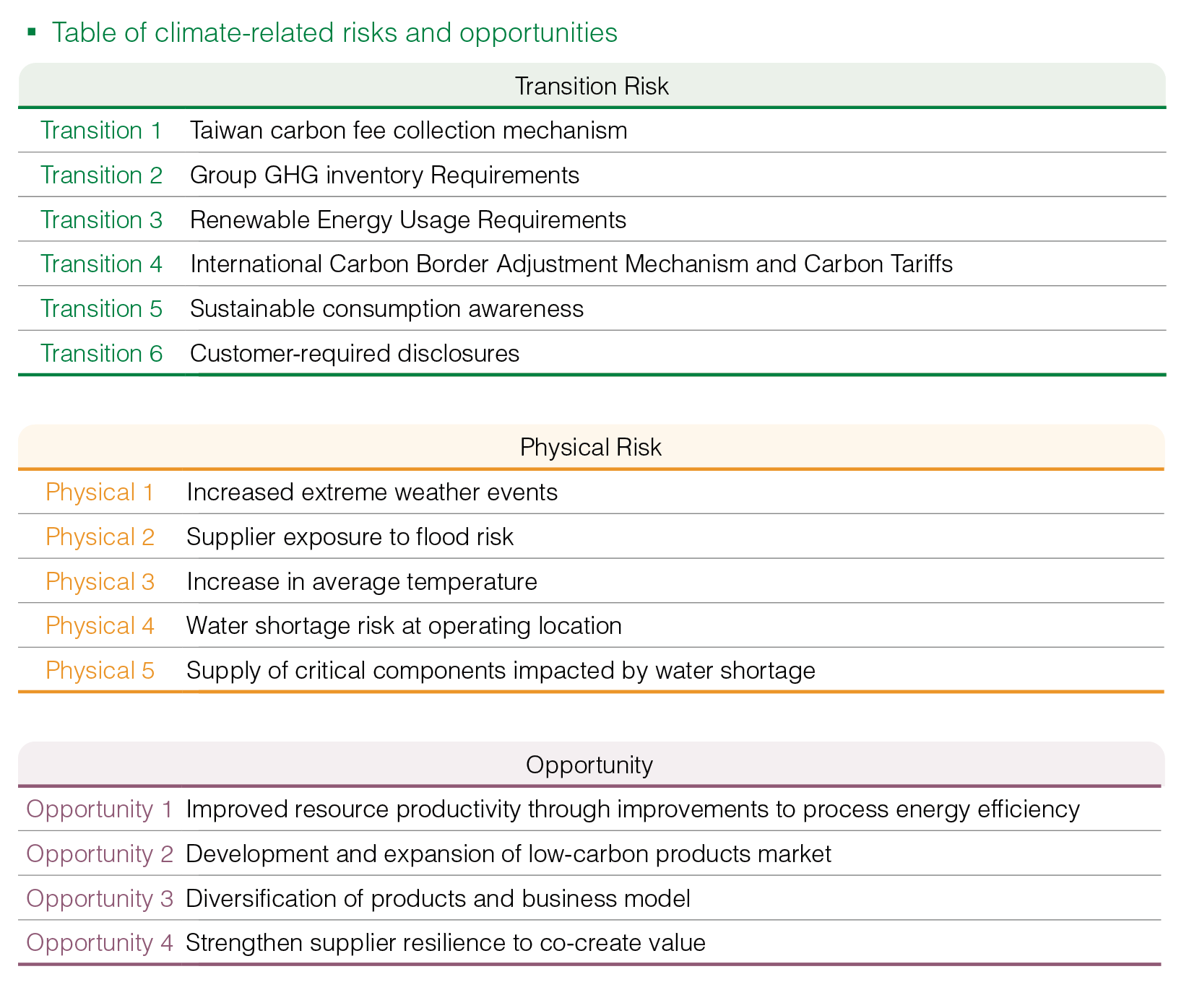
2024 GIGABYTE Climate-related Risks and Opportunities
The following are summaries of identified climate-related risks and opportunities. For more details, please refer to the TCFD Report.
Existing Laws and Regulations
| Risk Description | Taiwan carbon fee mechanism | Group GHG inventory Requirements | Renewable Energy Usage Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Medium-term | Immediate Future | Medium-term |
| Impact and Scope |
|
|
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE |
GIGABYTE carbon emissions are relatively low so the levying of carbon fees is expected to have little impact |
Fines for non-compliance with inventory a disclosure regulation |
Payment of energy fees, purchase of certificates, or payment of charges for statutory compliance |
| Response Measure |
GIGABYTE is continuing to monitor climate-related legislation in Taiwan. Measures such as the Sustainability Fund, internal carbon pricing, and carbon source management have been introduced already. We will continue to study low-carbon business models to counter the operational impact of rising carbon costs |
The existing scope will be gradually expanded until all overseas branches of locations are covered. GHG inventory data quality and verification will be continuously expanded as well. |
We are currently installing photovoltaic equipment in Taiwan already. In the future, we will assess purchased electricity as well as the feasibility of building our own solar power plants at overseas plants to continue improving the green electricity usage of the Group. |
| Risk Description | International Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism and Carbon Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Long-term |
| Impact and Scope |
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Payment of carbon tariffs when importing products or participation in the local emissions control and carbon credit trading mechanism in accordance with the regulations of the target market |
| Response Measures | GIGABYTE is continuing to monitor international climate-related legislation. A carbon footprint calculation and management system has already been introduced and supply chain carbon management will be further strengthened going forward. |
| Risk Description | Increasing awareness of sustainable consumption |
|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Medium-term |
| Impact and Scope | Operation: Failure to meet consumer expectations will affect product sales. Downstream: Impact on product sales and revenue. |
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | An increase in marketing costs to strengthen the Companyʼs image as a green brand when EU/US markets where there is greater awareness of sustainable consumption are important export markets for GIGABYTE. |
| Response Measures |
Continued promotion of ESG and sustainability-related activities as well as regular publication of the Sustainability Report and TCFD Report to enhance consumer perception on the Companyʼs sustainability developments. We will also actively participate in international sustainability ratings and achieve good results to strengthen the Company’s sustainability image. |
| Risk Description | Disclosures and compliance with sustainability-related requirements from customers |
|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Immediate Future |
| Impact and Scope | Operation: Failure to meet customer requirements will result in lost customers and orders. Downstream: Impact on product shipments and revenue. |
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Stricter customer requirements on sustainable supply chain management when B2B products account for a growing proportion of GIGABYTE sales. |
| Response Measures | GIGABYTE will continue to publish sustainability-related information on open platforms to give stakeholders a better idea of our sustainability strategy. We also communicate regularly with stakeholders to ensure that the information conforms to customer requirements and expectations on disclosure. |
Physical Risk
| Risk Description | Increasing extreme weather events | Supplier exposure to flood risk |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Immediate Future | Medium-term |
| Impact and Scope |
|
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Loss of production from production interruption due to extreme weather events and cost of post-disaster recovery. | Identify suppliers in coastal or riverside cities, particularly critical suppliers for key products. Flooding of the supply chain will impact on procurement costs, production output, and revenue. |
| Response Measures |
Establish the “Risk and Emergency Management Guidelines” in accordance with ISO 14001 to formulate the management and response measures for typhoons and floods. Diversification and distribution of product sources in the supply chain to improve the stability of material supply and strengthen the risk resilience of the supply chain |
Sustainable supplier evaluations are conducted every year to evaluate how well suppliers are responding to climate change in order to reduce climaterelated potential risks for supply chain management. |
| Risk Description | Increase in average temperature | Water shortage risk at operating location | Supply of critical components impacted by water shortage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Medium-term | Medium-term | Immediate Future |
| Impact and Scope |
|
Operations: may come under pressure or be disrupted completely due to water shortages. |
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Higher energy costs from increase in operating time and cooling intensity of air-conditioning equipment due to high temperatures. | Loss of production from operation interruption due to drought and cost of post-disaster recovery. | Interruption of critical parts supply due to drought may impact on the shipping volume of high-end products. This increases purchasing costs or may lead to missed orders. |
| Response Measures | Continue to introduce temperature and power supply management systems for offices and plants. Gradually retire and replace aging equipment, and optimize the energy utilization efficiency of the equipment. | Water shortage drills are regularly conducted at plants to prepare for strict water restrictions caused by extended droughts. Water reclamation systems and water storage equipment are installed in plants. Employees are constantly reminded of the importance of saving water | Climate risk research is conducted on the supplierʼs location to assess their ability to respond to climate change. Diversification and distribution of product sources in the supply chain improve the stability of material supply and strengthen the risk resilience of the supply chain |
Climate Opportunities
| Opportunity Description | Enhancement of resource productivity through improving process energy efficiency |
|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Medium-term |
| Impact and Scope |
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Annual savings in energy costs and avoidance of non-cost-effective investments required for achieving compliance with laws or customer requirements within a short time. |
| Response Measures | The process power management and monitoring system has now been introduced at the Headquarters to improve energy efficiency and optimize time-of-use. At the same time, automated production processes are being progressively introduced at our three main production factories. These not only improve output and reduce non-conformities but also decrease wastage. |
| Opportunity Description | Development and expansion of the low-carbon products market | Diversification of products and business model |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Immediate Future | Medium and Long-term |
| Impact and Scope | Operation: Increased production costs from investment in new equipment and R&D of low-carbon products. Downstream: Improvement in product energy efficiency reduces energy costs during use. |
Upstream: Customized materials and technical support are provided by suppliers in support of solutions. Operation: Increased revenue by creating products and services with higher unit price levels through product diversification. Downstream: Reduction in energy costs during product use and waste disposal costs. |
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Revenue created by high-value and low-carbon products as well as energy efficiency benefits customers. | Revenue created by green and low-carbon products and services has high values and a recyclability ratio. |
| Response Measures |
Allocate part of annual revenue to research and development to innovate environmentally friendly products with high performance and low carbon footprint The Green Sustainable Development Committee sets up and supervises the implementation of sustainability strategy. Meetings are periodically convened to monitor and supervise implementation progress. |
GIGABYTE will continue to develop high-performance computing servers, reverse logistics services for electronic products, calculate all product carbon footprints, publish product environmental reports, provide public disclosures on the CSR website, and fulfill due diligence on product management. |
| Opportunity Description | Strengthen supplier resilience Co-create value |
|---|---|
| Impact Timeframe | Medium-term |
| Impact and Scope |
|
| Financial Impact on GIGABYTE | Reduction or diversification of purchasing costs away from vendors located in regions with high climate-related risks to reduce potential climate-related losses in the supply chain. |
| Response Measures | The “Sustainable Supplier Evaluation Questionnaire” is conducted for key suppliers every year; climate-related risk assessment and research are also conducted on related suppliers. The supplier conference is held every year with local industry leaders, sustainability experts and instructors sharing climate risk strategies and practices. |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Management Performance
GIGABYTE GHG reduction pathway is based on a 50% reduction in 2025 compared to the base year of 2009. GHG inventory is also conducted in accordance with ISO 14064, Scope of inventory was expanded from 2021 onwards in response to new regulatory requirements. The Taipei Silicon Valley Park Office where the subsidiaries Bestyield International, G-Style, and Selita Precision as well as the sub-subsidiary GIGAPIC are located were incorporated into the original inventory boundary. Inventory and disclosure of the Group’s Scope 3 emissions were also added. Air pollution control complied with local regulations in Taiwan and China with no NOX, SO, and PFCs were emitted by production processes and products.
Progress on GHG Reduction Targets
| Scope 1+2 Targets | 2024 Targets Completed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute reduction | Intensity reduction | ||
| Short-term | Carbon reduction of 3% every year | Reduction of 14.31% compared to last year | Carbon emission per Million NTD in revenue 55% reduction compared to last year |
| Medium & Long-term | Carbon reduction of up to 50% in 2025 compared to 2009 (base) | Reduction of 51.97% compared to 2009 (base year) Carbon emission per Million NTD in revenue | Carbon emission per Million NTD in revenue 92.17% reduction compared to 2009 (base) |
Note 1: The new 2022 electricity coefficients published by the National Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC, on December 20, 2024, was reduced, so GIGABYTE’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions met the target of a 50% reduction compared to the 2009 base year in 2024, ahead of schedule.
Note 2: The difference in scope of the GHG inventories in 2024 and base year was due to the inclusion of the Taipei Silicon Valley Park Office where the subsidiaries
Scope 1-2 GHG emissions of GIGABYTE in the recent 4 years
| (Unit: t-CO2e) | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 Emissions | 1,063.52 | 627.81 | 832.86 | 824.73 |
| Scope 2 Emissions | 28,874.43 | 27,283.64 | 26,606.40 | 22,687.85 |
| Total (Scope 1+2) | 29,937.95 | 27,911.44 | 27,439.26 | 23,512.58 |
| Comparison with the Previous Year | +4.05% | -6.77% | -1.69% | -14.31% |
| Comparison with the Base Year (2009) | -38.85% | -42.99% | -43.95% | -51.97% |
Scope 3 GHG emissions of GIGABYTE in the recent 4 years
| (Unit: t-CO2e) | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect Emissions from Transportation | ||||
| Employee Commuting | 1,201.65* | 1,867.53* | 1,028.98* | 1,224.31* |
| Business Travel | 24.13* | 128.35* | 548.17* | 752.83* |
| Upstream Distribution and Transportation | 234.74 | 58.32 | 617.35 | 2,905.56 |
| Downstream Distribution and Transportation | 40,088.61 | 28,051.45 | 44,405.99 | 20,416.20 |
| Indirect Emissions from Products Used by GIGABYTE | ||||
| Purchased Goods | 1,515,136.60* | 892,256.60* | 1,213,983.28* | 1,075,787.90* |
| Waste Generated in Operations | 1,464.50* | 1,238.66* | 1,911.11* | 2,238.90* |
| Capital Goods | 739.74 | 776.94 | 580.91 | 576.26 |
| Fuel- and Energy-related Activities (not included in scope 1 and 2) | 1,860.45 | 1,217.49 | 3,188.28 | 3,908.80 |
| Indirect Emissions Associated with the Use of GIGABYTEʼs Products | ||||
| Processing of Sold Products | 1,722.91 | 2,312.99 | 1,541.80 | 1,603.54 |
| Use of Sold Products | 4,239,140.03* | 5,689,602.28* | 4,525,119.43* | 5,434,613.16* |
| End-of-life Treatment of Sold Products | 10,931.82* | 8,089.73* | 8,757.16* | 9,738.99* |
| Total scope 3 emissions | 5,812,545.17 | 6,625,600.33 | 5,801,682.44 | 6,553,766.45 |
| Total scope 3 emissions verified by a third party | 5,767,898.72* | 6,593,183.15* | 5,751,348.11* | 6,524,356.09* |
Note 1: For progress towards the greenhouse gas emissions reduction target, please refer to CSR Performance – Environmental Aspect.
Note 2: Since 2021, the Scope 3 emission categories materially relevant to GIGABYTE have been verified by a third party. Figures that have been verified are marked with “✽”. Please find the verification statement at Quality and Environment Management Certification.
- Home
- Innovation Management
- The Guanxi Blue Zone
- The Ocean is Our Home
- From the Chairman
- Commitment to CSR
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Material Topics
- SDGs
- Corporate Organization
- Code of Conduct
- Information Security & Privacy
- Risk Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Tetralogy of Supply Chain Engagement
- Conflict Mineral
- Environmental Management Policy
- Brand Strategy and Business Reputation Management
- Climate Strategy and Risk Management
- Customer Relations Management
- Eco-friendly Product
- Extended Product Responsibility
- Biodiversity
- Circular Economy
- Green Action
- Sustainability/Environmental Education
- Green Activities
- Working Holiday
- Corporate Volunteering
- Go Green Taiwan
- Make Earth Green Again
- Tree Map
- Overview/Core Concept
- Rooftop Farm
- Ecology Photo Competition
- Resource Hub
- Diverse and Inclusive Workplace
- Talent Management
- Human Rights Management
- Talent Cultivation and Development
- Occupational Safety
- Health Care
- Upgrade Your Life
- Social Inclusion
- CSR Milestone
- Economic Aspect
- Environmental Aspect
- Social Aspect
- CSR Report
