GIGABYTE has long been dedicated to environmental issues. In addition to actively implementing actions to reduce carbon emissions, water usage, and waste, the company continuously strengthens its product stewardship and sustainable supply chain management to mitigate the negative impact of its operations and value chain on the ecosystem.
None of GIGABYTEʼs global operational sites are located in areas of high biodiversity importance. The company is committed to taking action within its own operations to avoid harming biodiversity, while also supporting the vision of “Zero Deforestation by 2050” and achieving “No Net Loss and Net Positive Impact on Nature.” To this end, GIGABYTE has established the Biodiversity and Zero Deforestation Commitment and initiated stakeholder engagement to enhance environmental well-being and co-create sustainable value.
■ GIGABYTEʼs Biodiversity Commitment: Please refer to the Biodiversity and No Deforestation Commitment.
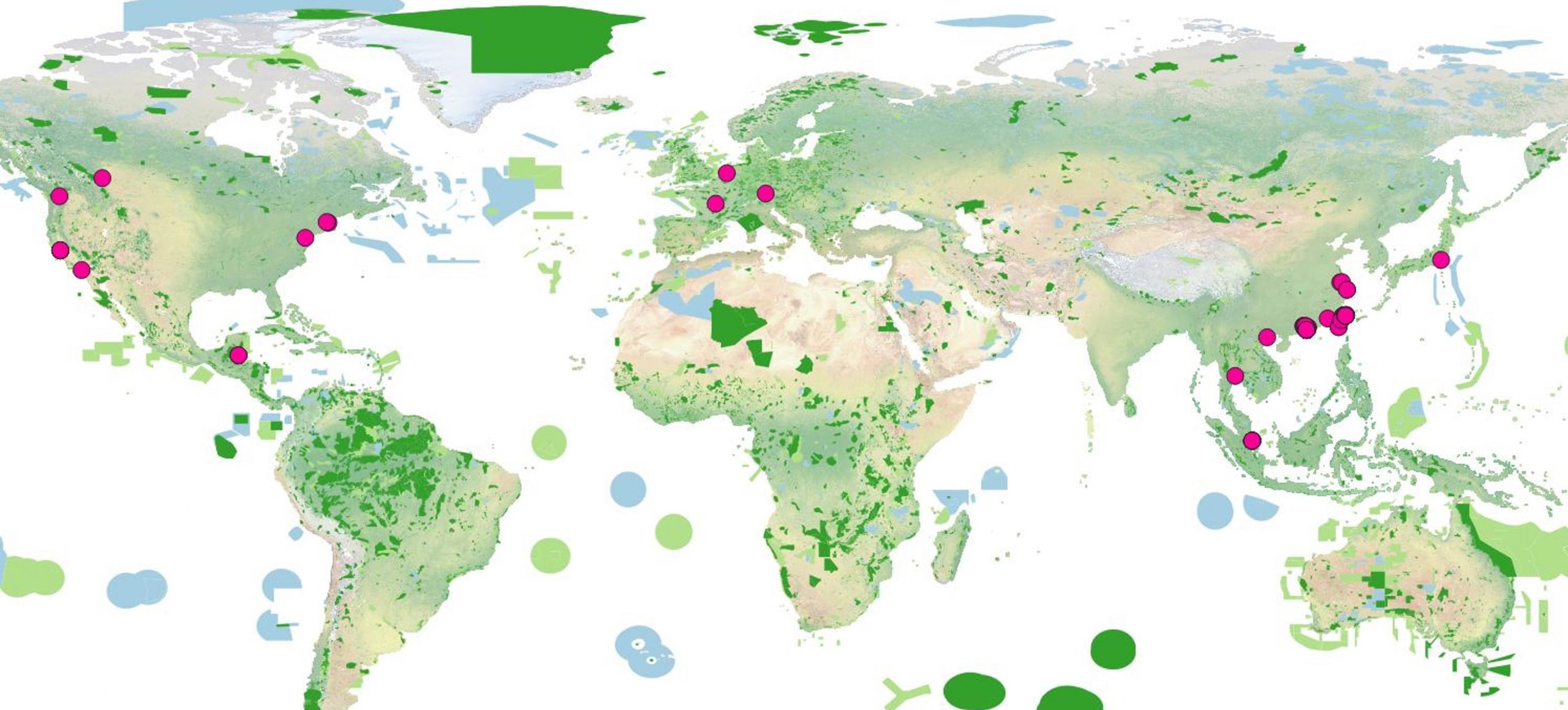
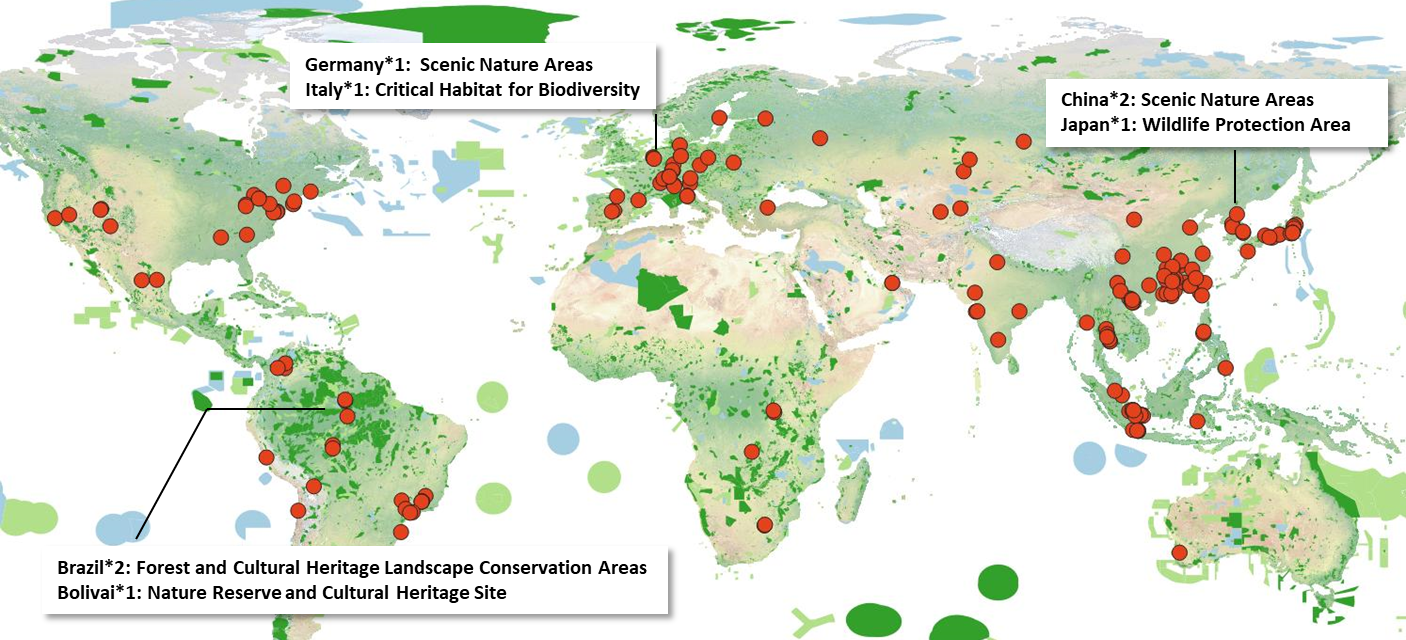
Value Chain Operational Sites and Biodiversity Conservation Areas
GIGABYTE Used the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) definitions of biodiversity conservation areas, GIGABYTE conducted overlay analyses of its operational sites, top 100 suppliers, upstream smelters, and downstream service locations.
The results showed that neither the value chain sites, nor the suppliersʼ headquarters are directly located within biodiversity conservation areas. However, 3% of smelters are directly situated in ecological protection zones. Moving forward, GIGABYTE will collaborate with value chain partners through management and advocacy efforts to reduce biodiversity impacts and create positive influence.
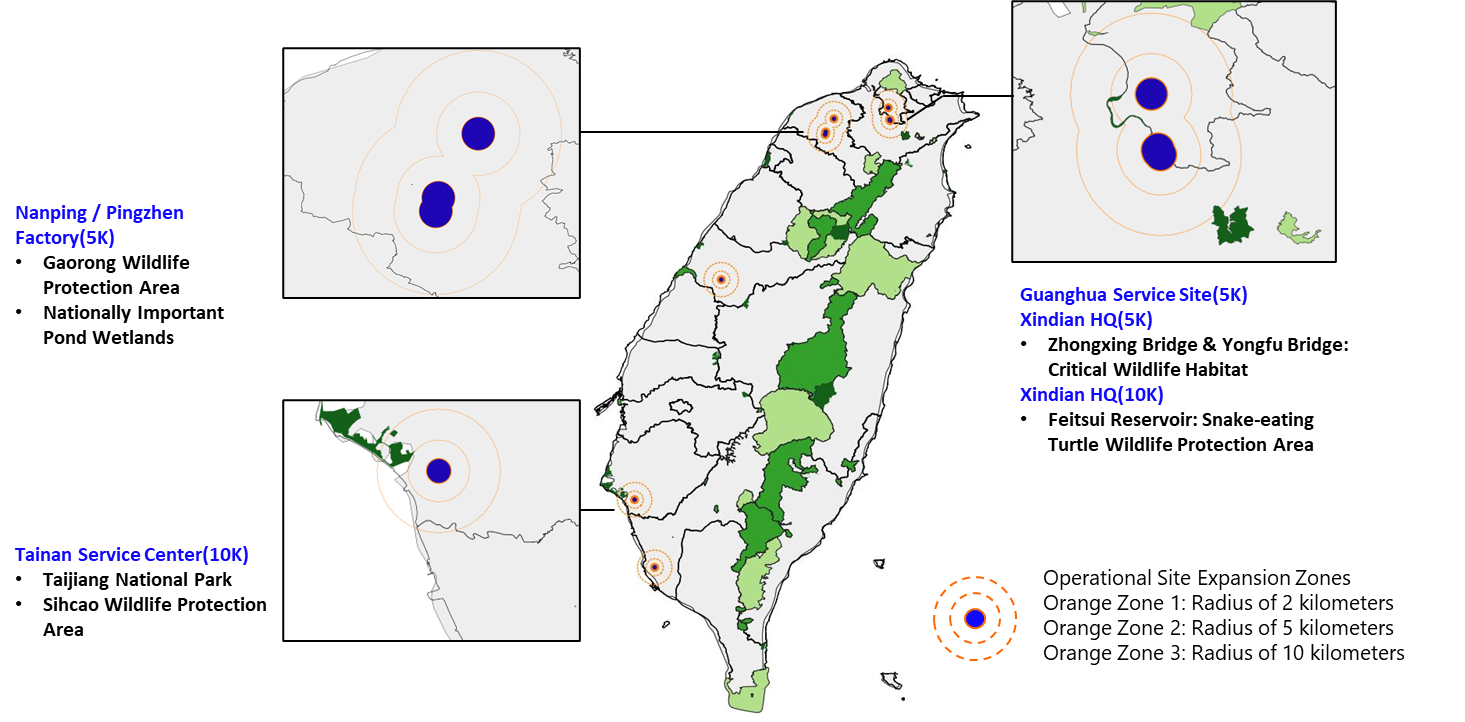
Taiwan Operational Sites and Downstream Service Locations with Biodiversity Conservation Areas
0% of top 100 suppliersʼ headquarters are directly located in ecological protection zones
3% of smelters are directly located in ecological protection zones
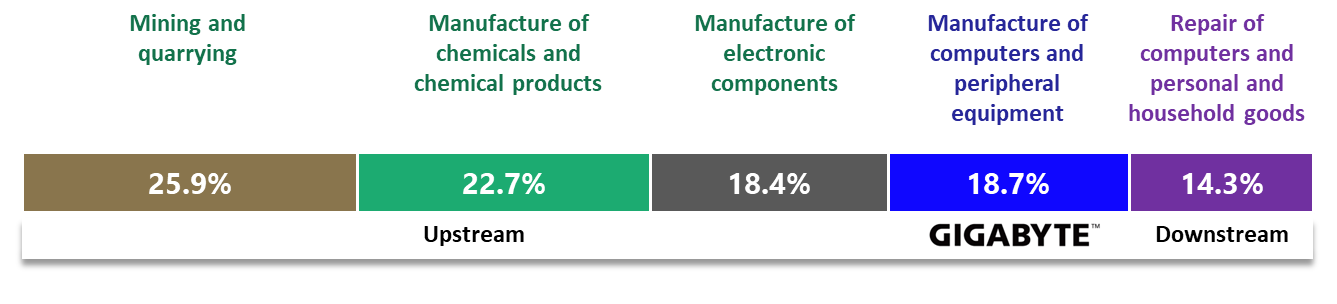
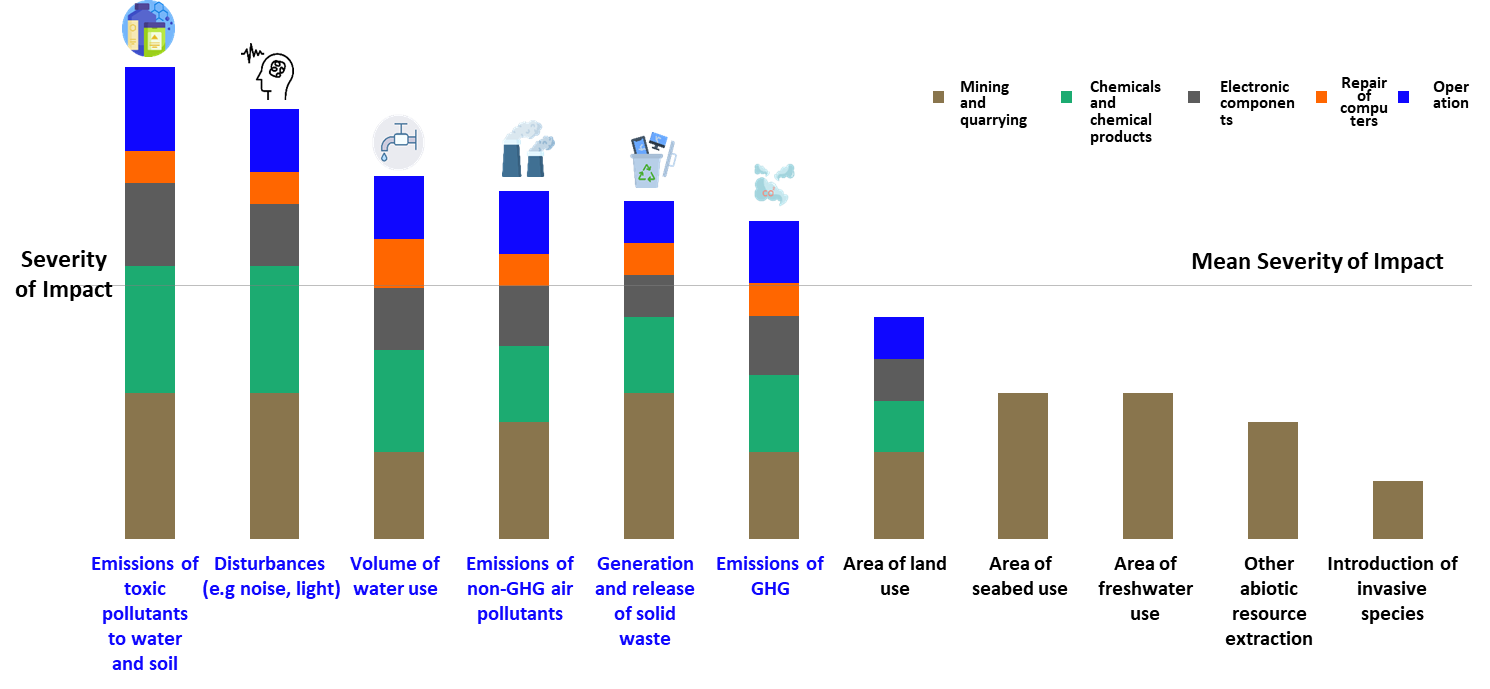
Environmental Impact Analysis of Value Chain Operations
GIGABYTE utilizes the ENCORE platformʼs database of key environmental impact factors across industries and conducts weighted analysis based on the value chainʼs dependency on natural capital. This process identified six major environmental impact factors potentially arising from value chain operations:
- Emission of hazardous substances into soil and water
- Disturbances such as noise and light pollution
- Volume of water use
- Non-GHG air pollution emissions
- Generation and discharge of solid waste
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Water resource consumption
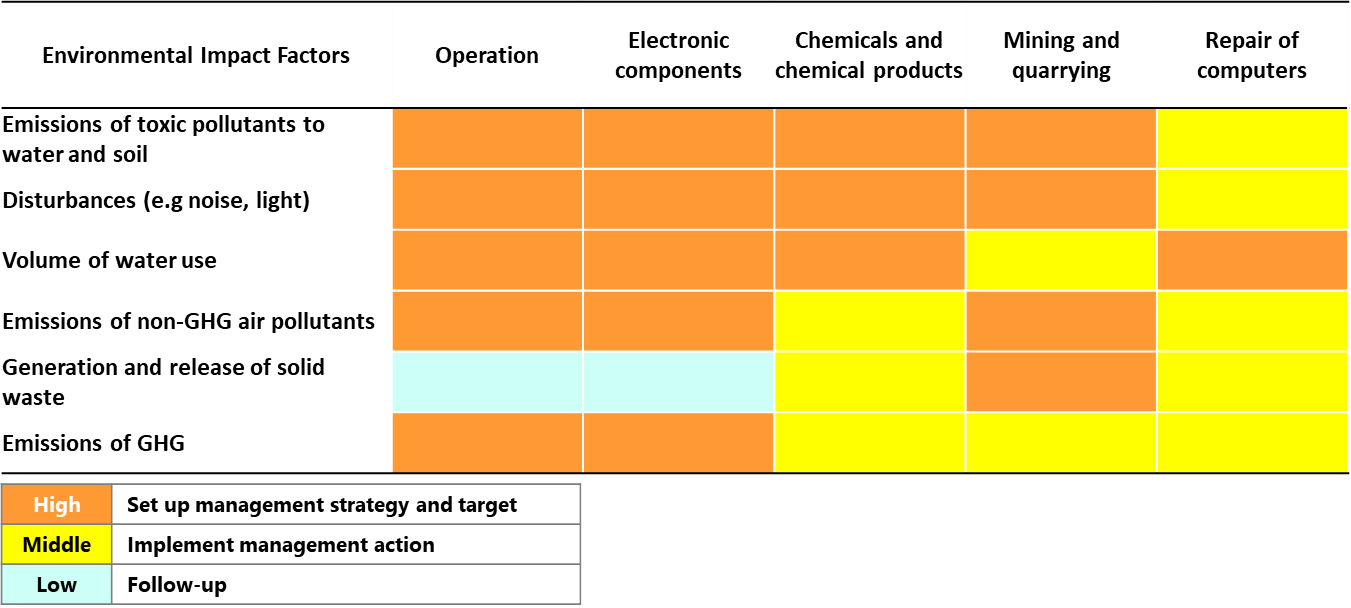
GIGABYTE further manages risks associated with significant impact factors.
Major Environmental Impact Drivers
Nature-Related Risk and Opportunity Management Strategy
Transition Risks
| Risk | Expansion of hazardous substance regulations | Stricter air emission regulations | Tighter waste disposal regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Emission of hazardous substances into soil and water | Non-GHG air pollution emissions | Generation and discharge of solid waste |
| Timeframe | Short-term | Long-term | Short-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
|
|
| Management Strategy |
|
Implement air emission monitoring and improvement |
|
| Risk | Ban on hazardous raw materials requiring alternatives |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Emission of hazardous substances into soil and water |
| Timeframe | Short to mid-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
| Management Strategy |
|
| Risk | Increased consumer awareness of product safety |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Emission of hazardous substances into soil and water |
| Timeframe | Short-term |
| Impact Scope | Operations: Enhance product verification and labeling to ensure safety |
| Management Strategy |
|
| Risk | Noise from manufacturing/testing affecting humans and wildlife |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Disturbances such as noise and light pollution |
| Timeframe | Short-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
| Management Strategy | Implement noise monitoring and improvement |
Physical Risks
| Risk | Soil/water pollution |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Emission of hazardous substances into soil and water |
| Timeframe | Mid-short term |
| Impact Scope |
|
| Management Strategy |
|
| Risk | Water scarcity | Smog and acid rain |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Volume of water use | Non-GHG air pollution emissions |
| Timeframe | Mid-term | Long-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
Upstream & Operations: Increased cost for cleanroom equipment |
| Management Strategy | Promote water resource management (e.g., conservation, reuse) |
|
Nature-Related Opportunities
| Opportunity | Rising demand for green products | Enhanced ESG ratings through positive brand image |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Hazardous substance emissions to soil/water | |
| Timeframe | Mid-Long term | Short-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
Operations: Conservation efforts help maintain ecosystem services of soil and water |
| Management Strategy | Invest in green product R&D and design |
|
| Opportunity | Growth of circular economy market |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Factor | Solid waste generation |
| Timeframe | Short-term |
| Impact Scope |
|
| Management Strategy | Develop circular economy services |
Biodiversity Management Strategy
GIGABYTE actively promotes biodiversity management, demonstrating its commitment to sustainable development. The strategy is built around four key pillars:
- Enhancing Operational Environmental Management – Monitoring and managing emissions related to manufacturing processes to reduce ecological disturbances.
- Implementing Product Stewardship – Promoting green design and recycling mechanisms to reduce environmental pollution from electronic waste.
- Managing Supplier Environmental Impact – Improving sustainability performance across the supply chain to build a sustainable value chain.
- Environmental Compensation Actions – Engaging in activities such as afforestation and habitat restoration to give back to nature.
Through diverse initiatives, GIGABYTE is committed to comprehensive biodiversity protection.
| Operational Environmental Management |
Product Stewardship |
Supplier Environmental Impact Management | Environmental Compensation Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Compensation Actions | Eco-Friendly Product | Supply Chain Management | The Ocean is Our Home |
| Climate Strategy and Risk Management | Extended Product Responsibility | Tetralogy of Supply Chain Engagement | Make Earth Green Again |
| Circular Economy | Conflict Minerals Management | The Guanxi Blue Zone |
- Home
- Innovation Management
- The Guanxi Blue Zone
- The Ocean is Our Home
- From the Chairman
- Commitment to CSR
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Material Topics
- SDGs
- Corporate Organization
- Code of Conduct
- Information Security & Privacy
- Risk Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Tetralogy of Supply Chain Engagement
- Conflict Mineral
- Environmental Management Policy
- Brand Strategy and Business Reputation Management
- Climate Strategy and Risk Management
- Customer Relations Management
- Eco-friendly Product
- Extended Product Responsibility
- Biodiversity
- Circular Economy
- Green Action
- Sustainability/Environmental Education
- Green Activities
- Working Holiday
- Corporate Volunteering
- Go Green Taiwan
- Make Earth Green Again
- Tree Map
- Overview/Core Concept
- Rooftop Farm
- Ecology Photo Competition
- Resource Hub
- Diverse and Inclusive Workplace
- Talent Management
- Human Rights Management
- Talent Cultivation and Development
- Occupational Safety
- Health Care
- Upgrade Your Life
- Social Inclusion
- CSR Milestone
- Economic Aspect
- Environmental Aspect
- Social Aspect
- CSR Report